Heart health is one of the most important aspects of overall well-being, and accurately monitoring it plays a vital role in diagnosing cardiovascular conditions. One of the most reliable tools used for continuous heart monitoring is the Holter monitor. It is a small, wearable device that records the heart’s electrical activity over an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours. This device helps detect irregularities that may not be captured during a standard electrocardiogram (ECG) performed in a clinical setting.
What Is a Holter Monitor?
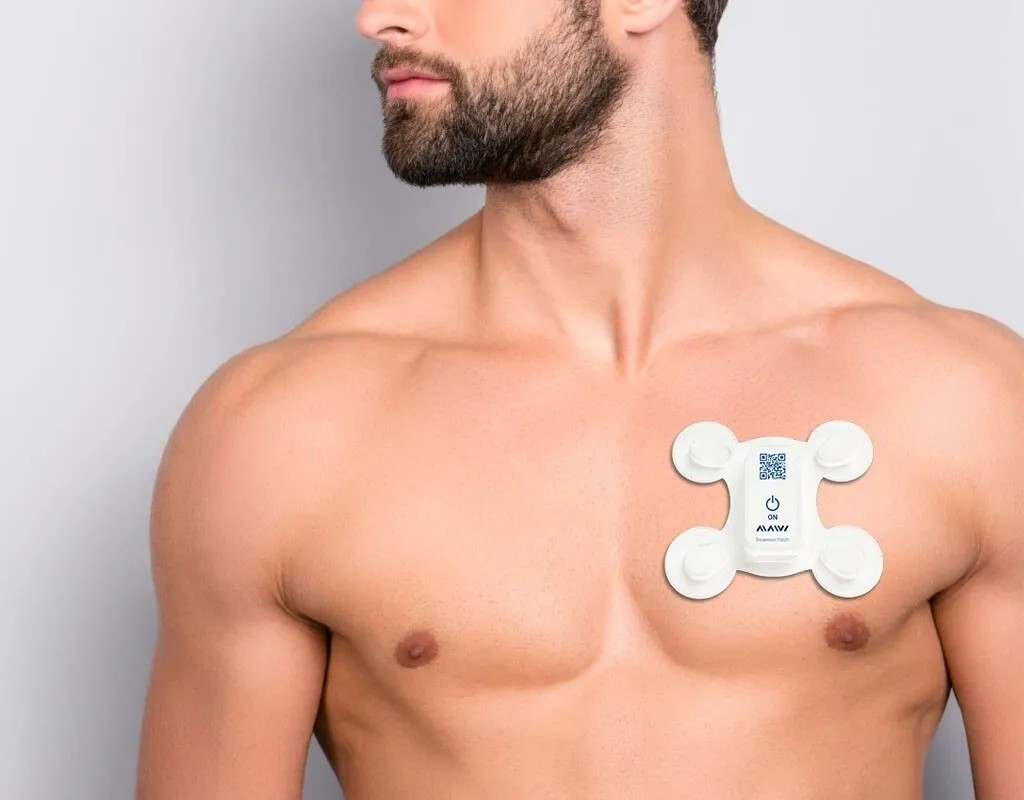
A Holter monitor is a portable device that continuously records the electrical signals of the heart. Named after Dr. Norman J. Holter, who developed the technology, the device is especially useful for identifying silent arrhythmias or intermittent heart issues that might not be present during a brief medical visit. It is about the size of a small camera and can be worn discreetly around the neck or attached to a belt.
The monitor is connected to the body through several adhesive electrodes placed on the chest. These electrodes detect the heart's electrical signals, which are then stored in the device for analysis. Once the monitoring period is complete, the recorded data is reviewed by a cardiologist to determine if there are any abnormalities in the heart’s rhythm or rate.
When Is a Holter Monitor Recommended?
Doctors typically recommend a Holter monitor when a patient experiences unexplained symptoms that could be related to an irregular heartbeat. These symptoms may include dizziness, fainting, palpitations, fatigue, or chest discomfort. If a standard ECG does not show any conclusive evidence of arrhythmias or other heart disorders, a Holter monitor can provide more comprehensive insight by tracking heart activity over a longer duration.
The device is also useful for monitoring the effectiveness of medications prescribed for heart rhythm issues. It helps determine whether a particular treatment is working or needs adjustment. In patients with pacemakers or other cardiac devices, the Holter monitor can evaluate the functionality of those implants as well.
How the Device Works
Once the Holter monitor is attached, the individual is advised to go about their normal daily routine. This allows the device to record the heart's activity during various activities, including rest, physical exertion, emotional stress, and sleep. The patient may be asked to keep a diary noting any symptoms experienced, along with the time they occurred. This helps correlate the symptoms with the recorded heart data.
The Holter monitor functions silently and does not interfere with daily activities. However, the patient is usually advised to avoid bathing or swimming during the monitoring period, as water can damage the device. Once the monitoring session ends, the device is returned to the medical facility, and the stored information is analyzed.
Advantages of Using a Holter Monitor
One of the key advantages of using a Holter monitor is its ability to provide a continuous record of heart activity over time. This is crucial because some heart conditions, such as intermittent arrhythmias, may not occur during a short ECG session. By capturing data around the clock, the device offers a more accurate and realistic picture of how the heart functions during daily life.
Another benefit is its non-invasive nature. The procedure is simple, painless, and does not require hospitalization. It allows patients to remain active and engaged in their regular activities while still undergoing medical evaluation. Additionally, it is an effective tool in the early detection of heart disorders, helping initiate timely intervention and potentially preventing more severe complications.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its usefulness, the Holter monitor has some limitations. It may not always capture rare or sporadic arrhythmias if they do not occur during the monitoring period. In such cases, doctors may recommend extended event recorders or implantable loop recorders that monitor heart activity for longer durations.
There is also a possibility of artifacts or disturbances in the recording caused by poor electrode contact, patient movement, or external electrical interference. Proper patient instruction and careful electrode placement help reduce these errors.
Recent Advances in Monitoring Technology
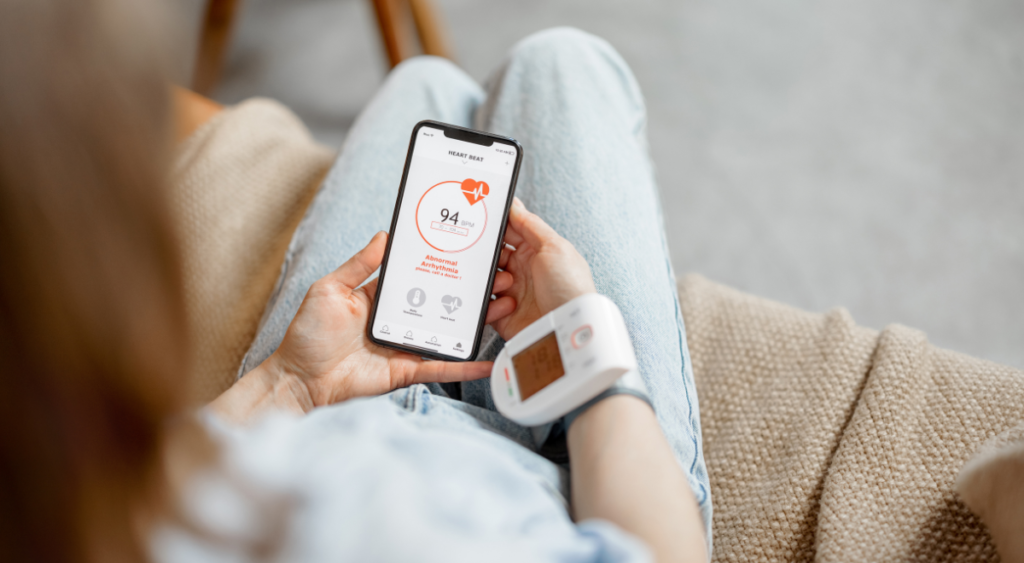
With advancements in wearable technology, newer Holter monitors are now smaller, wireless, and more comfortable. Some devices can transmit real-time data to healthcare providers via mobile networks, allowing for quicker intervention if needed. The integration of artificial intelligence into analysis software has also made it easier to detect subtle abnormalities that may have been previously overlooked.
Modern Holter devices are now capable of monitoring for extended periods, some up to 7 days or more, without compromising patient comfort. These improvements have significantly enhanced diagnostic accuracy and patient experience.
Conclusion
The Holter monitor remains a cornerstone in modern cardiology for diagnosing and managing various heart conditions. It bridges the gap between brief clinical evaluations and the need for continuous monitoring, capturing vital information that would otherwise go unnoticed. As wearable technology continues to evolve, the role of devices like the Holter monitor in proactive heart care is becoming even more essential. For individuals experiencing unexplained cardiac symptoms, this simple yet powerful tool can provide the clarity needed for appropriate treatment and long-term heart health.